Matsy
Tools for Matched Series Analysis [v1.3 Dec-2025]
A pair of molecules are Matched Molecular Pairs if they differ in structure at a single substitutable position; that is, they have the same scaffold but different R groups. A Matched Molecular Series generalises the concept of Matched Pairs to N molecules (N >= 2) that share the same scaffold but have different R groups at the same position.
While Matched Pair analysis has had some success particularly in the area of physical property prediction, it has been less successful for biological activity prediction. In recent work published in J. Med. Chem. [1], in collaboration with AstraZeneca we have shown that longer Matched Series are much better at predicting R groups likely to improve activity.
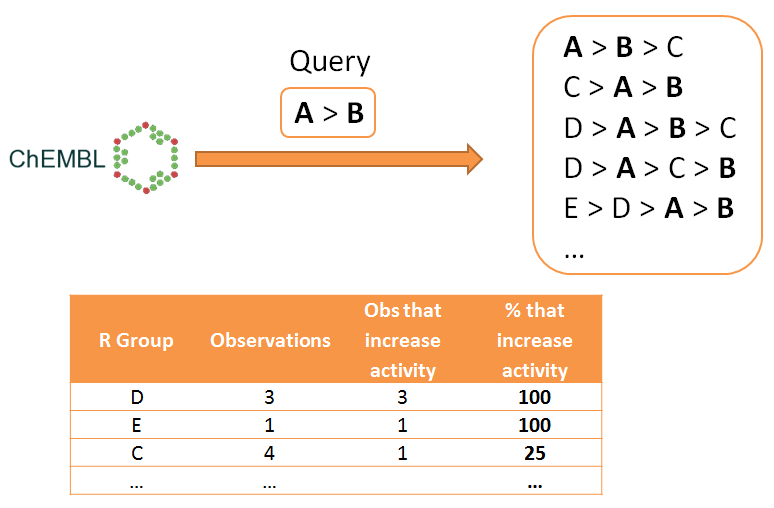
Matsy (short for "Matched Series") is a set of software tools to generate and search a database of matched series, and to use the database to predict R groups most likely to increase activity (or some other property) further given a particular observed order of R groups so far. An overview of the predictive method is shown below.
References
1. O'Boyle, N. M.; Boström, J.; Sayle, R. A.; Gill, A. Using Matched Molecular Series as a Predictive Tool To Optimize Biological Activity. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2014, 57, 2704. [Open Access]
Further info
- A presentation on the visualization and manipulation of Matched Molecular Series for decision support presented at the ACS meeting in Boston, August 2015 [PDF]
- A presentation describing how to update the Topliss decision tree using Matched Molecular Series data presented at the ACS meeting in San Francisco, August 2014 [PDF]
- A presentation giving an overview of the Matsy algorithm, "Evidence-based medicinal chemistry", presented at the UK QSAR meeting in Cambridge (UK), Sept 2014 [PDF]
The following video demonstrates using the Matsy GUI to check Topliss Tree predictions:
